Platforms
This page describes the use of the different platforms we support.
The general rule we apply for assigning IP addresses follows the following numbering order:
1 - Router
2 - Low-level computer (Raspberry Pi)
3 - High-level computer
4 - Additional component (e.g. Franka Arm)
5 - LiDAR
So for example, if we connect the Ouster LiDAR to the Lynx, we assign the Ouster with IP address 10.15.20.5.
Franka
Simulation Franka
A Franka arm can be launched in simulation by creating a configuration with an Arm of type franka.
Hardware Franka
The robot needs to be connected with it’s control box.
Flip the switch on the control box to start the robot.
An ethernet cable should connect the control box with the network.
By default, we connect the control box with the router of the Panther.
The web interface can be reached on the statically assigned address:
10.15.20.4.
In the web-interface, settings can be changed and the joints can be (un)locked. The mode can also be changed to the required FCI mode.
Panther
Simulation Panther
A Panther vehicle can be launched in simulation by creating a configuration with a Vehicle of type Panther. Note that the E-Stop is triggered by default and needs to be released before driving is possible. This can be done by a service call:
ros2 service call /panther/hardware/e_stop_reset std_srvs/srv/Trigger {}
Hardware Panther
Enable the battery (switch at the front of the robot).
Start the robot (press red power button).
Wait until the E_STOP animation is played
Release hardware stop (rotate red emergency button if it was pressed).
Start the Logitech gamepad:
press Logitech button.
press mode button if mode light is on (should be off).
put the switch at the back on X.
Remove the E_STOP by Left Trigger + A on the gamepad.
You can drive by pressing Left Button and use the two joysticks.
You can enable the E_STOP by pressing B.
See this for more information about gamepad control.
One can enable the high voltage system of the Panther (for example to power an Arm) using a service call:
ros2 service call /panther/hardware/aux_power_enable std_srvs/srv/SetBool "{data: true}"
The robot can be shut down as follows:
Shut down the robot (hold red button next to battery switch till it starts blinking).
Wait until all lights are off.
Disable the battery (switch at the front of the robot)
Configuration Panther
When the Panther is started, two WiFi networks (Panther_<serial_number> and Panther_5G_<serial_number>) should be available. One can connect with one of the WiFi networks or connect using a ethernet cable directly to the Teltonika. After connecting, it should be possible to ssh into all three computers.
Teltonika RUTX11:
This is an industrial router. The Raspberry Pi 4 and Lenovo ThinkStation P360 are connected to the Teltonika by Ethernet. Also the Velodyne Lidar and is connected to the Teltonika by Ethernet. A combo antenna (the black dome) is also connected, which enables the Teltonika to obtain a GPS location.
Raspberry Pi 4 :
The Raspberry Pi 4 is built in the front of the Panther and not directly accessible. Two Docker images are pre-installed: a docker image of the panther_ros repository and a docker image of the joy_to_twist repository. Both images are started automatically when the robot starts, as do all docker images installed on the Pi. The first image runs all the required software to use the robot, like motor control and led control. The second image enables gamepad control with the Logitech gamepad shipped with the robot, when the USB receiver is connected to the USB port at the front of the robot.
We have also cloned the nmea-gps-docker repository with a docker that enables use of GPS in ROS. This docker images gets started automatically as well when the the Panther starts. For more information about the use of this docker, see the Sensors section.
Lenovo ThinkStation P360
The Lenovo ThinkStation P360 is a powerful computer, used to handle the camera stream. We can run our docker image on this built in computer.
Lynx

Simulation Lynx
A Lynx vehicle can be launched in simulation by creating a configuration with a Vehicle of type Lynx.
Hardware & Configuration Lynx
This section is equivalent to the Hardware Panther and Configuration Panther sections, except for the namespace here being lynx and the Lenovo ThinkStation P360 will be replaced with a different computer.
Realsense
Simulation Realsense
A Realsense camera can be launched in simulation by creating a configuration with an Camera of type realsense.
Hardware Realsense
One can use a Realsense by connecting it with the host device using USB.
ZED
Simulation Zed
A ZED camera can be launched in simulation by creating a configuration with an Camera of type zed.
Hardware Zed
A ZED camera can be used by connecting it to the host device via USB. To allow non-root users to access the camera, UDEV rules must be installed on the host machine. The required script can be found here.
Ouster
Simulation Ouster
An Ouster lidar can be launched in simulation by creating a configuration with a Lidar of type Ouster.
Hardware Ouster
Network settings:
When using the Ouster lidar, make sure that the IP-address of the host device (where the Ouster node is running) is set correctly in the settings of the Teltonika router. One can assign a static IP address to the Ouster via the Teltonika interface. In case of the Husarion vehicles, this interface is reachable via http://10.15.20.1/, and the static IP address should be set to 10.15.20.5 as number 5 is reserved for LiDARs.
Additionally, it is important to assign the correct UDP destination IP address for the Ouster LiDAR. This can both be done via the Ouster’s configuration interface at http://os-{serial_number}.local/, or it can be done via the launch file of the Ouster (ouster.launch.py in the rcdt_sensors package).
Note: If the firewall is enabled in Ubuntu, communication with the LiDAR is most likely blocked. Unblock it by allowing the IP-address of the LiDAR:
sudo ufw allow to {IPv4_address}
sudo ufw allow from {IPv4_address}
ROS2 setup:
The Ouster driver runs as a LifeCycle node, meaning that once created, the node starts in an Unconfigured state. It needs to be configured and activated to start the driver.
Find all of the connected Ouster’s information at http://os-{serial_number}.local/, where the following parameters for the driver node can be found:
sensor_hostname: Dashboard > System Information > IPv4 (Remove the prefix length)udp_dest: Dashboard > System Status > Web Client Address
Velodyne
Simulation Velodyne
A Velodyne lidar can be launched in simulation by creating a configuration with a Lidar of type velodyne.
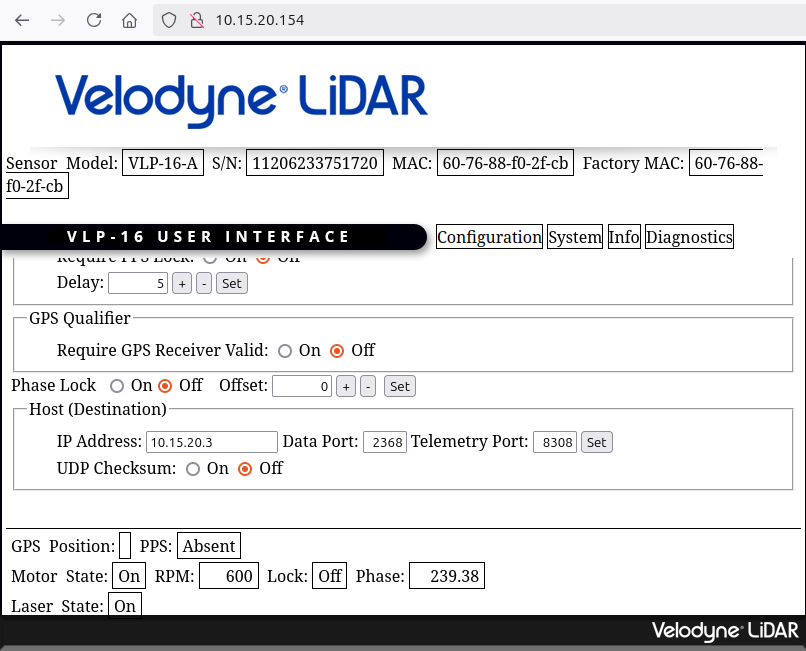
Hardware Velodyne
When using the Velodyne lidar, make sure that the IP-address of the host device (where the velodyne node is running) is set correctly in the settings. One can edit the settings of the velodyne using a web interface on it’s IP-adress.
|
|
|---|
Teltonika GPS
Simulation Teltonika
A Teltonika GPS can be launched in simulation by creating a configuration with an GPS of type teltonika.
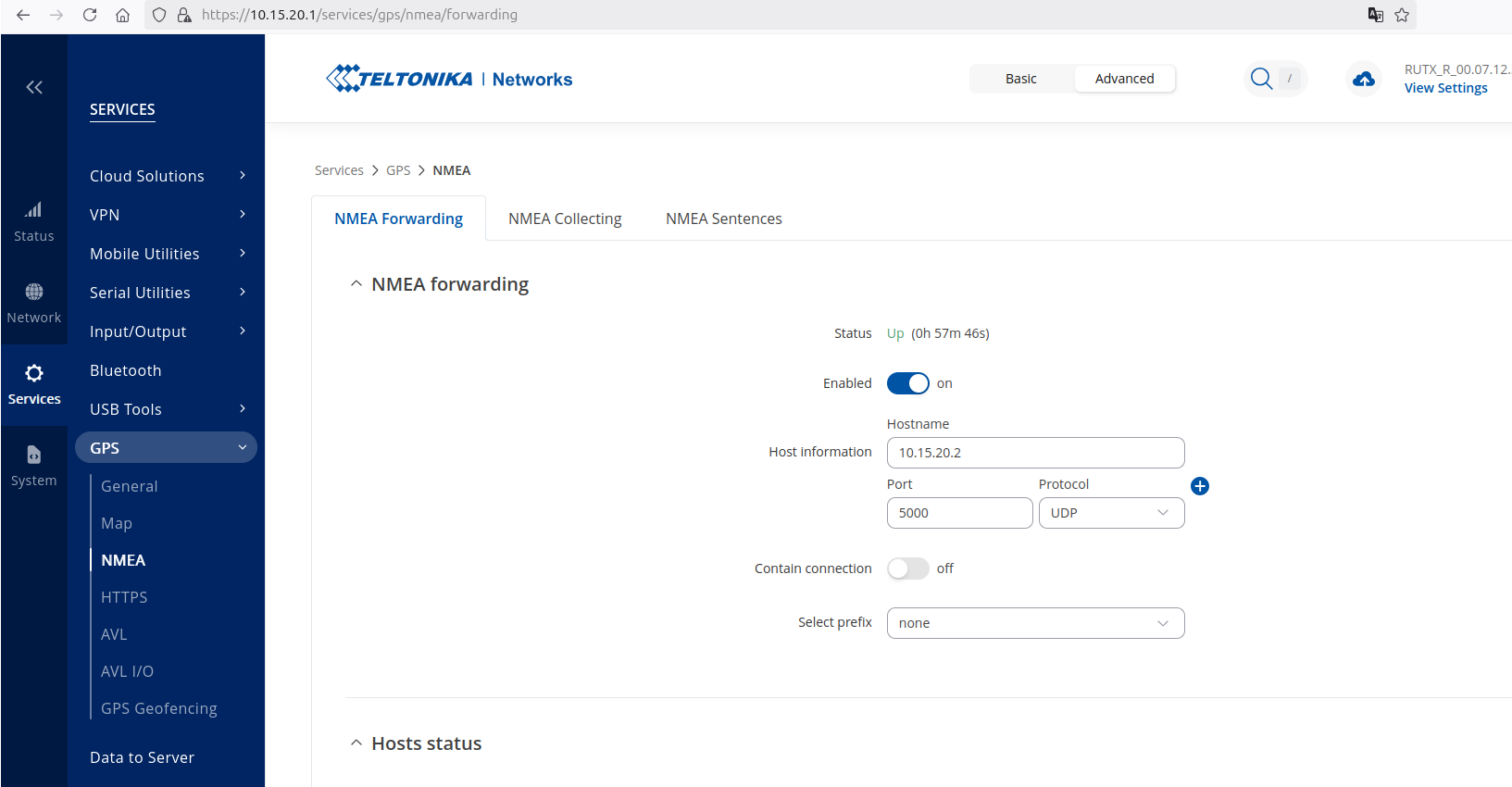
Hardware Teltonika
When using the Teltonika GPS, make sure that the IP-address of the host device (where the nmea node is running) is set correctly in the settings. One can edit the settings of the Teltonika using a web interface on it’s IP-adress.